Content
- Calculating the Double Declining Depreciation Method
- Double Declining Balance Method Example
- How to calculate depreciation using the double declining method
- Example of the Double Declining Depreciation Method
- Declining Balance Depreciation – Explained
- Advantages of Double Declining Balance Depreciation

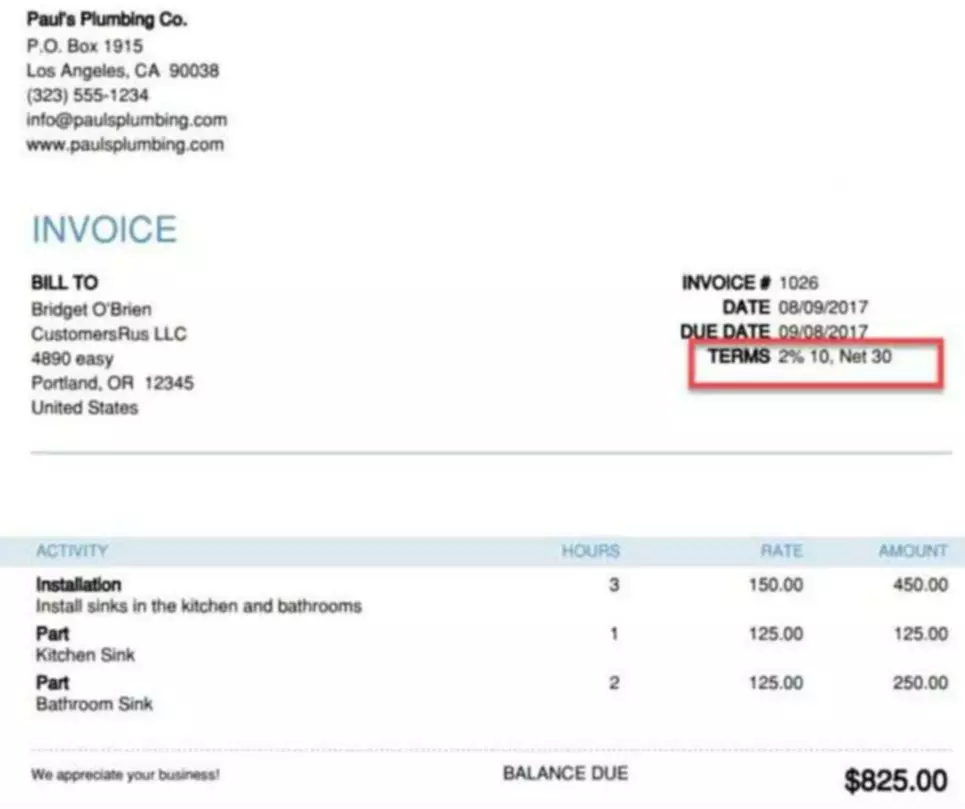
So, after we record Year 2 depreciation, the book value of the work truck is now $33,620. That’s the book value ($41,000) minus the depreciation ($7,380). So, after we record Year 1 depreciation, the book value of the work truck is now $41,000. That’s the book value ($50,000) minus the depreciation ($9,000). Remember, every accounting term is going to stay a little hazy until you work through a couple examples.
If the salvage value of an asset is known , the cost of the asset can subtract this value to find the total amount that can be depreciated. Assets with no salvage value will have the same total depreciation as the cost of the asset. As a business owner, you need to know that the transition from one accounting method to another is inevitable. You should ask your accountant about their approach to calculating the value of depreciation for different assets. In the initial years, you tend to get more money back from the tax write-offs. You can use this amount to offset the asset’s purchase price. If you have taken a loan to finance the asset’s purchase, you can quickly pay off a more significant chunk of that loan.
Calculating the Double Declining Depreciation Method
By applying the DDB depreciation method, you can depreciate these assets faster, capturing tax benefits more quickly and reducing your tax liability in the first few years after purchasing them. Therefore, such revisions are made prospectively so that the remaining depreciable base is spread over the remaining life. Method involves calculations that are quite similar to the straight-line method, but it allocates the depreciable base over the units of output rather than years of use. Or, a printing machine may produce an expected 4,000,000 copies.
Under the straight-line method, the 10-year life means the asset’s annual depreciation will be 10% of the asset’s cost. Under thedouble declining balance method the 10% straight line rate is doubled to 20%. However, the 20% is multiplied times the fixture’s book value at the beginning of the year instead of the fixture’s original cost. Double Declining BalanceIn declining balance method of depreciation or reducing balance method, assets are depreciated at a higher rate in the initial years than in the subsequent years. A constant depreciation rate is applied to an asset’s book value each year, heading towards accelerated depreciation. Some companies use accelerated depreciation methods to defer their tax obligations into future years. Double declining balance depreciation is one of these methods.
Double Declining Balance Method Example
Then record the depreciation journal entry in Year 2 as a debit of $7,380 to the Depreciation Expense-Business Truck account and a credit of $7,380 to the Accumulated Depreciation-Business Truck account. Then record the depreciation journal entry in Year 1 as a debit of $9,000 to the Depreciation Expense-Business Truck account and a credit of $9,000 to the Accumulated Depreciation-Business Truck account.
We also reference original research from other reputable publishers where appropriate. You can learn more about the standards we follow in producing accurate, unbiased content in oureditorial policy. Kirsten Rohrs Schmitt is an accomplished professional editor, writer, double declining balance method proofreader, and fact-checker. She has expertise in finance, investing, real estate, and world history. Kirsten is also the founder and director of Your Best Edit; find her on LinkedIn and Facebook. If you have expensive assets, depreciation is a key accounting and…
How to calculate depreciation using the double declining method
Instead, the asset will depreciate by the same amount; however, it will be expensed higher in the early years of its useful life. The depreciation expense will be lower in the later years compared to the straight-line depreciation method. Given the nature of the DDB depreciation method, it is best reserved for assets that depreciate rapidly in the first several years of ownership, such as cars and heavy equipment.
- (You can multiply it by 100 to see it as a percentage.) This is also called the straight line depreciation rate—the percentage of an asset you depreciate each year if you use the straight line method.
- Salvage ValueSalvage value or scrap value is the estimated value of an asset after its useful life is over.
- In regards to depreciation, salvage value is the estimated worth of an asset at the end of its useful life.
- Kirsten Rohrs Schmitt is an accomplished professional editor, writer, proofreader, and fact-checker.
- Adam Hayes, Ph.D., CFA, is a financial writer with 15+ years Wall Street experience as a derivatives trader.
With this method, the depreciation is expressed by the total number of units produced vs. the total number of units that the asset can produce. Conceptually, depreciation is the reduction in the value of an asset over time due to elements such as wear and tear. Continue the steps in every accounting year till the useful life of the asset is over.
However, you should be aware of the method your company uses to maintain its books of accounts. It’s always best to have a rationale for why you’re using a particular method and the purpose the method serves for your new business. Once you fully depreciate the asset’s value, you have to record the salvage value of the asset and close the account. Currently, 20% of $32,000 will be reduced from the book value. The process has to be continued until you reach the asset’s salvage value that becomes equal to the asset’s book value. If you start writing off your asset early on, your tax obligation will reduce significantly.
- You’ll need to pay taxes directly to the IRS via quarterly estimated tax payments.
- You can use this amount to offset the asset’s purchase price.
- Harold Averkamp has worked as a university accounting instructor, accountant, and consultant for more than 25 years.
- However, you still can’t depreciate an asset to a value less than its salvage value with the hard limit of zero.
- After 10 years, it would be worth $3,000, its salvage value.
Toward the end of its useful life, the vehicle loses a smaller percentage of its value every year. First, Divide “100%” by the number of years in the asset’s useful life, this is your straight-line depreciation rate. Then, multiply that number by 2 https://quickbooks-payroll.org/ and that is your Double-Declining Depreciation Rate. In this method,depreciation continues until the asset value declines to its salvage value. The beginning book value is the cost of the fixed asset less any depreciation claimed in prior periods.
Deixe uma resposta